Out-of-the-box Xprotect policies
Xprotect instances come with Three out-of-the-box Xprotect Host policies, one for the supported OS families (Linux, macOS, and Windows). The out-of-the-box policies are a great way to push some common and vital Application Control rules to the hosts in your instance and monitor the hosts before you create and push custom Xprotect policies to the hosts.
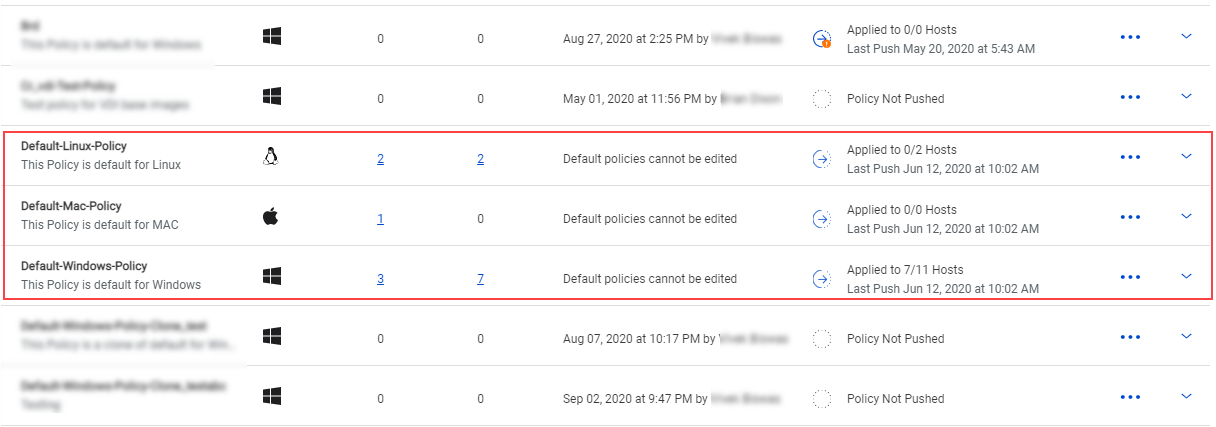
The out-of-the-box Xprotect policies are referred to as 'Default policies' in the Xprotect UI and the documentation. The Default policies are listed as Default-Linux-Policy, Default-Mac-Policy, and Default-Windows-Policy, on the Policies page in the Xprotect UI.
By design, you cannot edit Default policies; this applies to the stacks, rules, and Policy settings. Default policies are meant to be used only with ColorTokens-recommended rules and settings.
ColorTokens may update/change the stacks, rules, and Policy settings in the Default policies to provide added security based on the latest findings and trends. Updated Default policies move to the 'Applied' state. You must push the updated Default policies to the hosts to apply the revised rules are Policy settings. See Push policies to hosts for more details.
Stacks and rules in Default policies
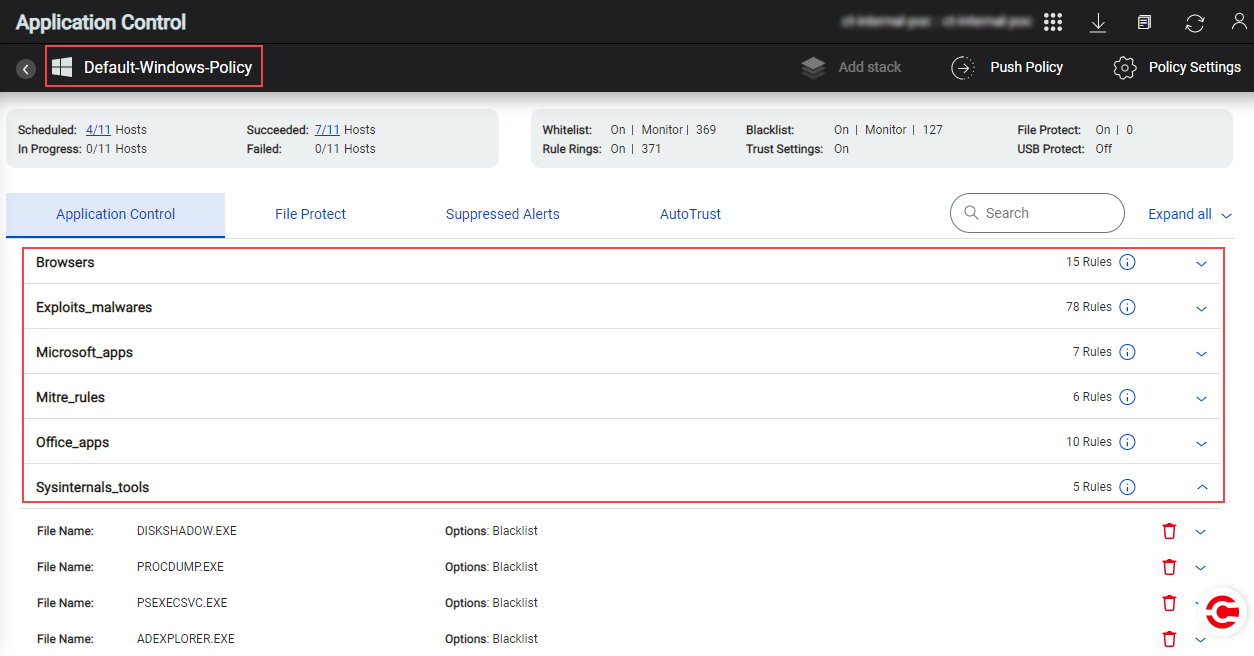
The stacks and rules in the Default policies are created based on the host-usage patterns by the OS family, current threat trends for an OS family, and the findings and recommendations from industry experts and ColorTokens Product Development and Threat Hunting teams.
|
Default policies contain only Application Control rules. The stacks and the types and number of rules in the default policies differ and depend on the OS family for which a Default policy is intended.
|
Policy settings for Default policies
|
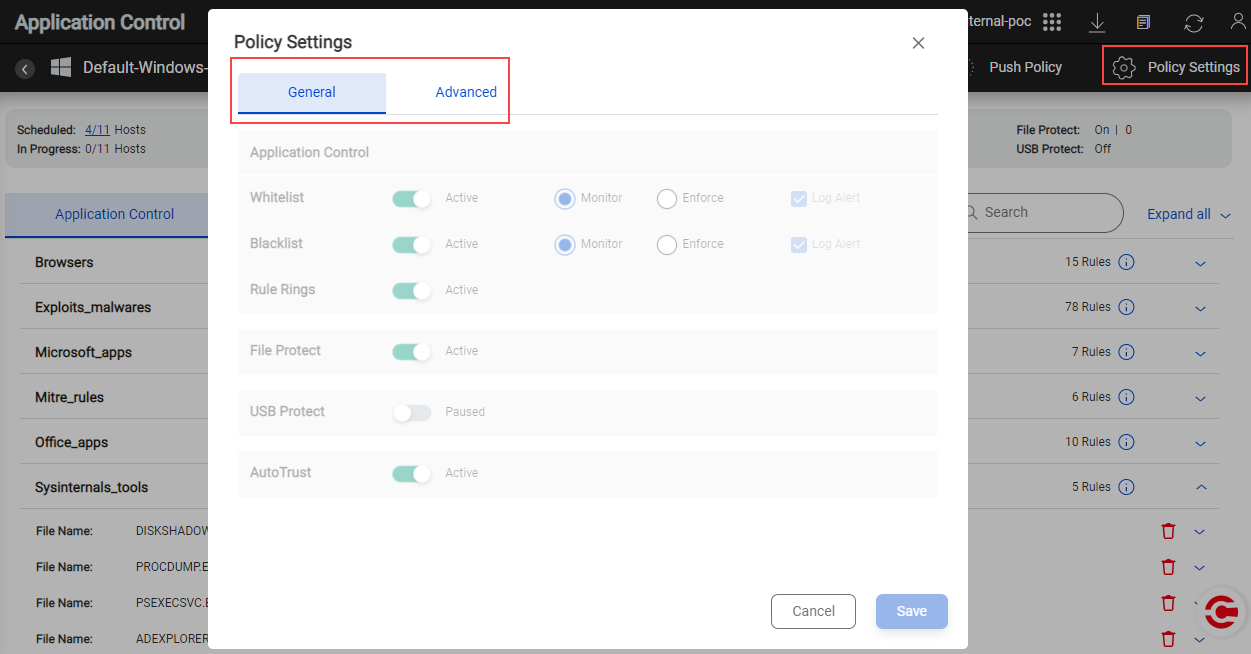
The Policy settings for the Default policies are set with a balanced approach to monitor and block processes. Alerts are generated when the Application Control rules in the policies are violated. See Alerts for more details.
|
General settings
-
Whitelist and Blacklist rules are Active. Policy violations are only monitored, and alerts are generated.
-
Rule Rings rules are Active. Policy violations are only monitored or enforced (block or kill processes) by the controls specified in the individual Rule Rings rules. Alerts are generated for both monitored and enforced violations.
-
File Protect rules are Active.
-
USB Protect is Paused.
-
AutoTrust setting is Active. The AutoTrust setting ( in the AutoTrust tab) is set to monitor processes that pose an 'Unknown risk' and block applications that pose 'High risk'.
-
The alerts generated by Xprotect agent services are suppressed ( in the Suppressed Alerts tab).
Advanced settings
-
The option to set the duration between operations performed on the hosts ( Agent Fetches Command Every selector) is set to One minute.
-
All TCP connections (excluding loopback connections) are monitored without any exceptions ( Exclude Destinations). This means that all TCP-related Rule Ring rules are Active.
Push Default policies
For new Xprotect deployments, we recommend that you push Default policies to hosts as the first layer of protection on the hosts. You must push Default policies, just like you would push a custom policy. See Push policies to hosts for more details.
We recommend that you spend some time to see the stacks, rules, and Policy settings in the Default policies before you push them to the hosts.
Clone Default policies
Clone Default policies to create new policies by reusing some of the stacks and rules in a Default policy. See Clone policies for more details.